![]()
In the last decade, researches on developing new methods on genome sequencing have been grown dramatically. Beside many important genome sequencing research aims, the possibility to medically diagnose/predict a specific disease is especially crucial. This is normally done by DNA sequence (genome building blocks) comparisons between a patient’s sample (query) and a healthy (reference) DNA sequence.
Hundreds of individual sequenced genomes are expected for some medically relevant disease that this fact increases the cost and time interval data analysis. This is especially important in personalized clinical sequencing where sequencing the ‘healthy’ need large-scale sequencing and analysis. In order to make use of this explosive growth in the number of 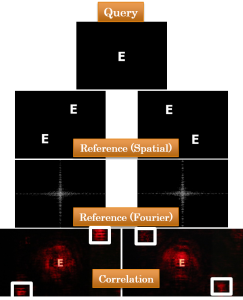 sequenced genomes, the scientific community requires tools that can quickly compare large numbers of long and highly similar sequences from whole genomes.
sequenced genomes, the scientific community requires tools that can quickly compare large numbers of long and highly similar sequences from whole genomes.
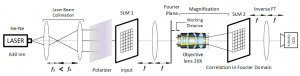
The general structure of the proposed optical DNA alignment system includes two main parts: A well-known procedure of global alignment, built upon utilizing an optical correlator, and a proposed novel local alignment algorithm. Global alignment phase, which handles very long sequences of A, G, C and T DNA characters through intrinsic optical parallel processing, locates regions with the highest similarity corresponding to approximate query location in the reference genome. At the first step, reference and query sequences are coded using an appropriate amplitude binary coding scheme. Then a correlation between the sequences are performed in the frequency domain utilizing a liquid crystal on silicon, LCOS, SLM as an optical correlator. Finally, the correlation output yields an approximate location of the query sequence in the reference sequence. The outputs of the optical global alignment structure are fed into the proposed local alignment algorithm, known as window-base matching algorithm, to compare each shorter read sequences with their corresponding matched part in the reference genome to detect and locate mutation types. The structure of DNA local sequence alignment utilizes a thresholding function in order to generate full and non-full peaks and analyses the sequence through specific length windows to immediately detect and locate any mutation in the query DNA sequence compared to the reference sequence.
Related Publication:
A novel multi-illumination photoacoustic imaging structure based on synthetic-aperture-radar (SAR) approach is proposed. In conventional photoacoustic imaging systems, due to the single illuminati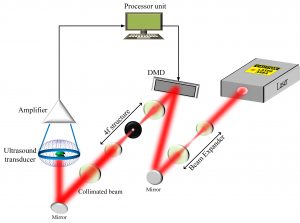 on direction of the laser source, the obtained image lacks resolution and resolution consistency in the whole image. Using multiple plane-wave illuminations from different directions help to improve filed-of-view and resolution of the system. The multi-view illumination helps in more complete capture of spatial frequency components which could be approved through a mathematical model of the system. Capturing more frequency components, in turn, results in the improved frequency bandwidth and thus resolution of the system. Simulation results shows 1.54dB and 0.03 improvements in image quality, based on peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index metric (SSIM) metrics compared to a conventional structure.
on direction of the laser source, the obtained image lacks resolution and resolution consistency in the whole image. Using multiple plane-wave illuminations from different directions help to improve filed-of-view and resolution of the system. The multi-view illumination helps in more complete capture of spatial frequency components which could be approved through a mathematical model of the system. Capturing more frequency components, in turn, results in the improved frequency bandwidth and thus resolution of the system. Simulation results shows 1.54dB and 0.03 improvements in image quality, based on peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index metric (SSIM) metrics compared to a conventional structure.
Related Publication:
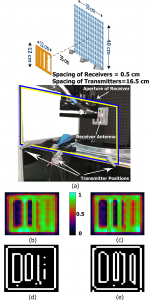
An effcient approach of designing multi-static arrays for millimeter-wave imaging, based on the k-space or Fourier-spatial domain characteristic of imaging systems is proposed. The goal is to decrease the redundancy of the data measured by each antenna, and to improve the resolution of the reconstructed image. The proposed technique is based on determining the role of each transmitter and receiver, in collecting the data from each voxel of the target in k-space domain and then rotating transmitters’ beams to measure the desirable information.
The effect of non-uniform redundant k-space domain frequency samples that act as an undesirable filter, is compensated using a modified SAR back-projection algorithm. Experimental and simulation results are compared with that of a sparse multi-static array with the same number of transmitters and receivers. Our simulations and measurements show significant improvement in terms of overall quality and edge preservation in the reconstructed images. Also, the obtained results demonstrate that using the proposed structure and algorithm, the average improvement in peak-signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index measure (SSIM) and digital image correlation (DIC) metrics of 3.03 dB, 0.22 and 0.173, are achieved, respectively.
Related Publication:
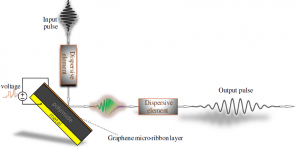
Ultrafast signal processing in the time domain with high resolution and reconfigurability is a challenging task. For the first time to our knowledge, a time-varying metasurface consisting of a graphene micro-ribbon array for implementing a time lens in the terahertz domain is designed.
Given that the surface conductivity of graphene is proportional to the Fermi energy level in the terahertz regime, it is possible to change the phase property of the incident electromagnetic pulse by changing the Fermi level while the Fermi level itself is a function of voltage. Upon this fact, a quadratic temporal phase modulator, namely, a time lens, has been realized. This phase modulation is applied to the impinging signal in the time domain.
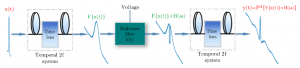 The terahertz time lens is a key element for processing of ultrafast temporal pulses. Using this time lens, a temporal filter in the terahertz regime is de-signed and simulated, which could have applications in terahertz communication and spectroscopy.
The terahertz time lens is a key element for processing of ultrafast temporal pulses. Using this time lens, a temporal filter in the terahertz regime is de-signed and simulated, which could have applications in terahertz communication and spectroscopy.
Related Publication:

تصویربرداری مادون قرمز به دلیل کاربردهای فراوانی که دارد در سالهای اخیر مورد توجه محققان قرار گرفته است. به ویژه به دلیل بی ضرر بودن امواج مادون قرمز برای بدن انسان، این ساختارها علاوه بر تصویربرداری صنعتی، در کاربردهای تشخیص پزشکی نیز مورد توجه قرار گرفته اند. سیستم تصویربرداری بررسی شده در اینجا سیستم تصویربرداری غیرفعال (بدون منبع) میباشد به گونهای که تشعشعات جسم توسط آشکارساز تک پیکسلی دریافت میگردد. آشکارسازهای مورد استفاده شامل دو نوع سنسور ابررسانای بالومتر و سنسور پایروالکتریک هستند. هدف، بهبود کیفیت تصاویر با جبران سازی اثرات مخرب بخش های مختلف سیستم در کیفیت تصویر میباشد. جهت بهبود کیفیت تصویر، در ابتدا تاثر بخشهای مختلف سیستم شامل آینه، روزنه موجد بر روی سنسور، سنسور و محیط مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. این بررسی بر اساس مدلسازی ریاضی سیستم تصویربرداری مادون قرمز بر اساس قوانین فیزیک نور و در نظر گرفتن اثر بخش های مختلف در این مدل، انجام شده است. پس از آن با در نظر گرفتن اثر مخرب هر بخش بر روی قدرت تفکیک و نویز تصویر، راهکارهایی جهت جبران هریک و بهبود کیفیت تصویر ارائه شده است. از جمله بررسیهای انجام شده می توان به این موارد اشاره نمود: بررسی اعوجاج آینه سهموی موجود در سیستم و جبران آن، دریافت تصویر با اندازه های مختلف روزنه روی سنسور و انتخاب ابعاد بهینه روزنه بر اساس تحلیل های تئوری و نتایج عملی، بررسی نویز محیط کاهش اثر آن در سیستم عملی و با پردازش تصویر.
A novel approach for foreground extraction has been proposed based on a popular three-dimensional imaging technique in optics, called integral imaging. In this approach, multiple viewpoint images captured from a three-dimensional scene are used to extract range information of the scene and effectively extract an object or a person, even in the presence of heavy occlusion. The alg orithm consists of two parts: depth estimation and reconstruction of the targeted object at the estimated depth distance. Further processing of the resulting reconstructed image can lead to the detection of a face or a pedestrian in the scene, which may not otherwise be detectable due to partial occlusion in each of the views. The validity of our approach has been demonstrated by experimental results in different scenarios.
orithm consists of two parts: depth estimation and reconstruction of the targeted object at the estimated depth distance. Further processing of the resulting reconstructed image can lead to the detection of a face or a pedestrian in the scene, which may not otherwise be detectable due to partial occlusion in each of the views. The validity of our approach has been demonstrated by experimental results in different scenarios.
Experimental setup used for validating the proposed method through different scenarios.
Viewpoint images recorded by 25 cameras.
Reconstruction results shown in two different depth planes corresponding to first doll’s face and the second doll when 25 camera viewpoints are used.


Related Publication: