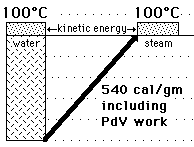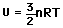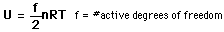Equipartition of Energy
The theorem of equipartition of energy states that molecules in thermal equilibrium have the same average energy associated with each independent degree of freedom of their motion and that the energy is

The equipartition result
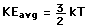 serves well in the definition of
kinetic
temperature since that involves just the translational degrees of
freedom, but it fails to predict the specific
heats of polyatomic gases because the increase in internal energy
associated with heating such gases adds energy to rotational and perhaps
vibrational degrees of freedom. Each vibrational mode will get kT/2 for
kinetic energy and kT/2 for potential energy - equality of kinetic and
potential energy is addressed in the virial theorem. Equipartition of
energy also has implication for electromagnetic radiation when it is in
equilibrium with matter, each mode of radiation having kT of energy in the
Rayleigh-Jeans
law.
serves well in the definition of
kinetic
temperature since that involves just the translational degrees of
freedom, but it fails to predict the specific
heats of polyatomic gases because the increase in internal energy
associated with heating such gases adds energy to rotational and perhaps
vibrational degrees of freedom. Each vibrational mode will get kT/2 for
kinetic energy and kT/2 for potential energy - equality of kinetic and
potential energy is addressed in the virial theorem. Equipartition of
energy also has implication for electromagnetic radiation when it is in
equilibrium with matter, each mode of radiation having kT of energy in the
Rayleigh-Jeans
law.
For the translational degrees of freedom only, equipartition can be shown to follow from the Boltzmann distribution.
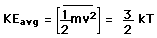 |
|
| Average thermal energy | Define constants |
| Specific heats of solids | Specific heats of gases |
Gas law concepts
Kinetic theory concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Thermodynamics | R Nave |